







ENTER YOUR DIMENSIONS
Select Your Spring Type
COMPRESSION
EXTENSION
TORSION
Select Your Unit of Measurement
Warning Messages
Table of Content:
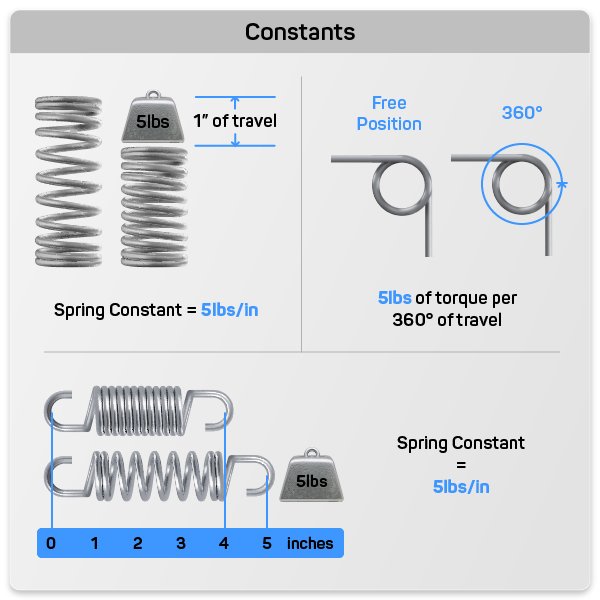
Spring constant is the amount of force required to move the spring a set amount of distance. The set amount of distance is determined by your units of measurement and your spring type.
For example, if you are calculating the spring constant of a compression spring using English measurements, your value would be pounds of force per inch of distance traveled. If you are using the metric system, your spring constant would be in Newtons per millimeter of distance traveled. Extension springs have the same units of measurements as compression springs, however, torsion spring constant is calculated in inch-pounds of force per 360 degrees of travel or per degree of travel.
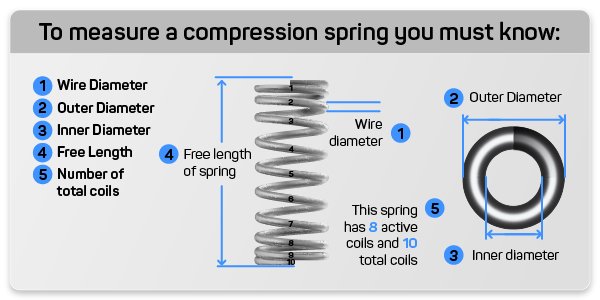
When determining a spring constant there are 2 different formulas you can use depending which information you have available to you. The first formula is the one most commonly used when you know the dimensions on yourof your spring but do not know your load and distance traveled on the spring.
k = Gd^4 / 8D^3N
k = Gd^4 / 8D^3N k = (11.5 x 10^6) (0.035)^4) / 8 (0.465)^3 (8) k = 17.2571875 / 6.434856 k = 2.68 lbs / inch
The other way to calculate the compression spring constant on your spring is if you know the load you want to achieve at a certain distance traveled. The formula to figure out your spring constant from a known load and distance traveled is:
Rate = Load / Distance Traveled
Rate = 2.5 pounds / inch
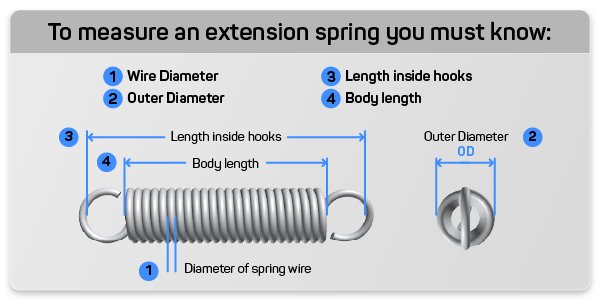
Calculating your extension spring constant uses the same formula as the compression spring constant calculation. Make sure when measure your extension spring you have the correct measurement for each value. For more information on this please visit our spring measurement and specifications page.
k = Gd^4 / 8D^3N
k = Gd^4 / 8D^3N k = (11.5 x 10^6) (0.044)^4) / 8 (0.381)^3 (5) k = 43.103104 / 2.21225364 k = 19.472 lbs / inch
The other way to calculate the extension spring constant on your spring is if you know the load you want to achieve at a certain distance traveled. The formula to figure out your spring constant from a known load and distance traveled is:
Rate = (Load – Initial Tension) ÷ Distance Traveled
For Example:
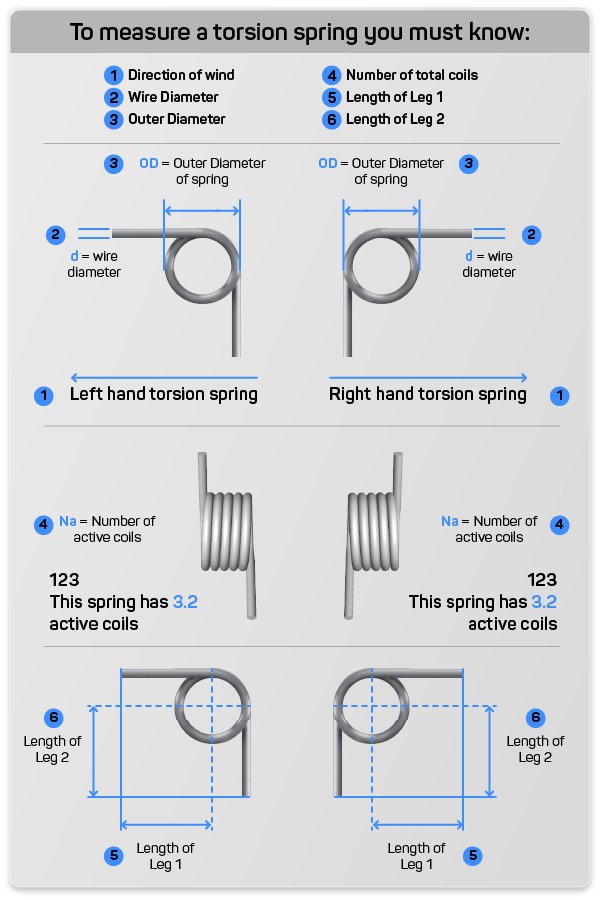
Calculating torsion spring constant is a little different than calculating the spring constant for compression or extension springs. Since a torsion spring travels in degrees and not linearly it needs a different formula. Below you can see the formula for torsion spring constant and an example of how the formula works.
(R) = Ed^4 / 10.8 DN
PSI x 10^6
Formula
Rate Per 360 degrees = Ed^4 / 10.8 DN
Spring constants are fundamental in the world of springs. They help us understand how springs behave under different conditions. Whether you're designing compression, extension, or torsion springs, knowing how to calculate spring constants is a game-changer.
But why go through all these calculations manually when you have Spring Creator 5.0? This advanced tool simplifies the process, making spring design a breeze.
Don't miss the opportunity to explore Spring Creator 5.0. It's your gateway to precision in spring design.
Unlock the world of spring constants and elevate your designs with Spring Creator 5.0. Try it today!
Created by Alfonso Jaramillo J
President Acxess Spring
Over 40 Years of Experience in Spring Engineering and Manufacturing
Your 3D is being generated, 3D generation Will take approximately 15 seconds. Your 3D Will load automatically on this page.

Your 3D is being generated, 3D generation Will take approximately 15 seconds. Your 3D Will load automatically on this page.
Spring Creator is an Acxess Spring Product, You will be redirected to acxesspring.com for your purchase
Click to open acxesspring.com
