







ENTER YOUR DIMENSIONS
Select Your Spring Type
COMPRESSION
EXTENSION
TORSION
Select Your Unit of Measurement
Warning Messages
Table of Content:
In today's fast-paced engineering landscape, precision and efficiency are paramount. The spring constant, a fundamental aspect of spring design, plays a pivotal role in your compression, extension, and torsion spring projects. This article is your gateway to mastering the art of spring constant units, which are measured in pounds of force per inch (lbf/in) or newtons per millimeter (N/mm) for compression and extension springs. For torsion springs, it's inch-pounds of torque per 360º (degrees) or inch-pounds of torque per degree in the imperial system, and newtons per millimeter per 360º (degrees) or newtons per millimeter per degree in the metric system.
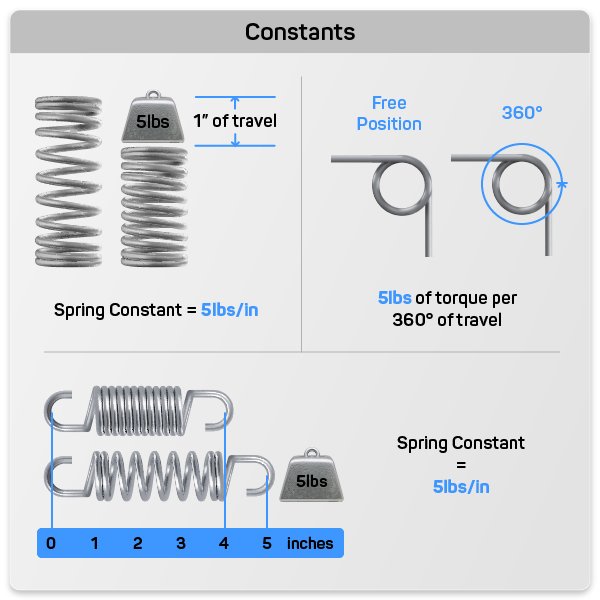
Compression And Extension Spring Rate
The spring constant is the linchpin of your compression and extension spring design, offering a linear force that you can fine-tune to meet your exact needs. Whether you're working with pounds of force (lbf) or newtons (N), the spring constant for load, or inches (in) and millimeters (mm) for travel, Spring Creator 5.0 provides the tools you need. Our formulas and diagrams will simplify the process, enabling you to calculate your compression or extension spring’s constant with precision and ease.
To calculate how much spring constant you need.
Use the formula k = F ÷ X to calculate the spring constant you require for your specific project. With Spring Creator 5.0, this task becomes a breeze.
To calculate spring constant of a spring.
D = D outer – d
G = E ÷ 2 ( 1 + V )
k = Gd^4 ÷ (8D^3 * na)
Incorporate these variables into the formula k = Gd^4 ÷ (8D^3 * na) to determine the spring rate or constant for your specific spring design. Our innovative Spring Creator 5.0 model feature simplifies the process, making it accessible and efficient for all your spring projects.
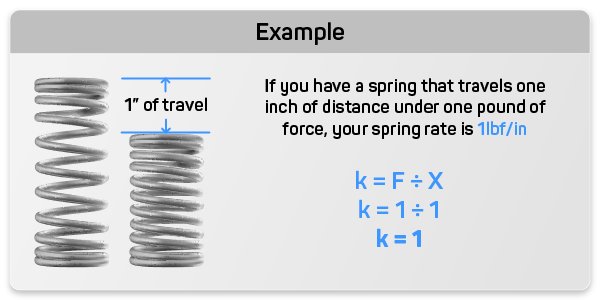
When it comes to torsion springs, understanding the spring constant is crucial for harnessing the radial force they provide. The torsion spring rate signifies the constant force or torque exerted per every 360 degrees of deflection, or even per a single degree of deflection.
R = Ed^4 / 10.8 DN R2 = R ÷ 360
Utilize the formula R = Ed^4 / (10.8DN) to determine the torsion spring rate per 360º (degrees). This is essential for a precise and functional torsion spring design.
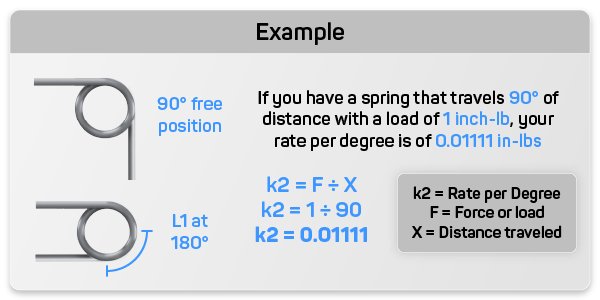
k = F ÷ X
For calculating the torsion spring rate per degree, use the formula k = F ÷ X. This enables you to determine the spring's constant on a degree-by-degree basis, ensuring precise performance in your torsion spring applications.
Welcome to the future of spring design. Spring Creator 5.0 brings precision and ease to your engineering projects, helping you harness the power of spring constants like never before. Whether it's compression, extension, or torsion springs, our innovative platform provides the tools you need to calculate spring constants, streamline your design process, and achieve engineering excellence. Don't wait—embrace the future with Spring Creator 5.0 today.
Created by Alfonso Jaramillo J
President Acxess Spring
Over 40 Years of Experience in Spring Engineering and Manufacturing
Your 3D is being generated, 3D generation Will take approximately 15 seconds. Your 3D Will load automatically on this page.

Your 3D is being generated, 3D generation Will take approximately 15 seconds. Your 3D Will load automatically on this page.
Spring Creator is an Acxess Spring Product, You will be redirected to acxesspring.com for your purchase
Click to open acxesspring.com
